Module 1: Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Introduction to Matter
introduction-to-matter
Physical Nature of Matter
physical-nature-of-matter
Particles Have Space Between Them
particles-have-space
Particles Attract Each Other
particles-attract
States of Matter
states-of-matter
Change of State: Effect of Temperature
change-of-state-temperature
Sublimation and Effect of Pressure
sublimation-pressure
Evaporation
evaporation
Summary & Practice Questions
summary-questions
Module 2: Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Pure Substances & Mixtures
pure-substances-mixtures
Types of Mixtures
types-of-mixtures
What is a Solution?
what-is-solution
Concentration of Solutions
concentration-of-solutions
Suspensions & Colloids
suspensions-colloids
Separation Techniques - Part 1
separation-techniques-1
Separation Techniques - Part 2
separation-techniques-2
Crystallisation
crystallisation
Physical & Chemical Changes
physical-chemical-changes
Elements & Compounds
elements-compounds
Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
States of Matter
Matter around us exists in three different states:
- 🧊 Solid
- 💧 Liquid
- 💨 Gas
These states arise due to variation in the characteristics of particles.
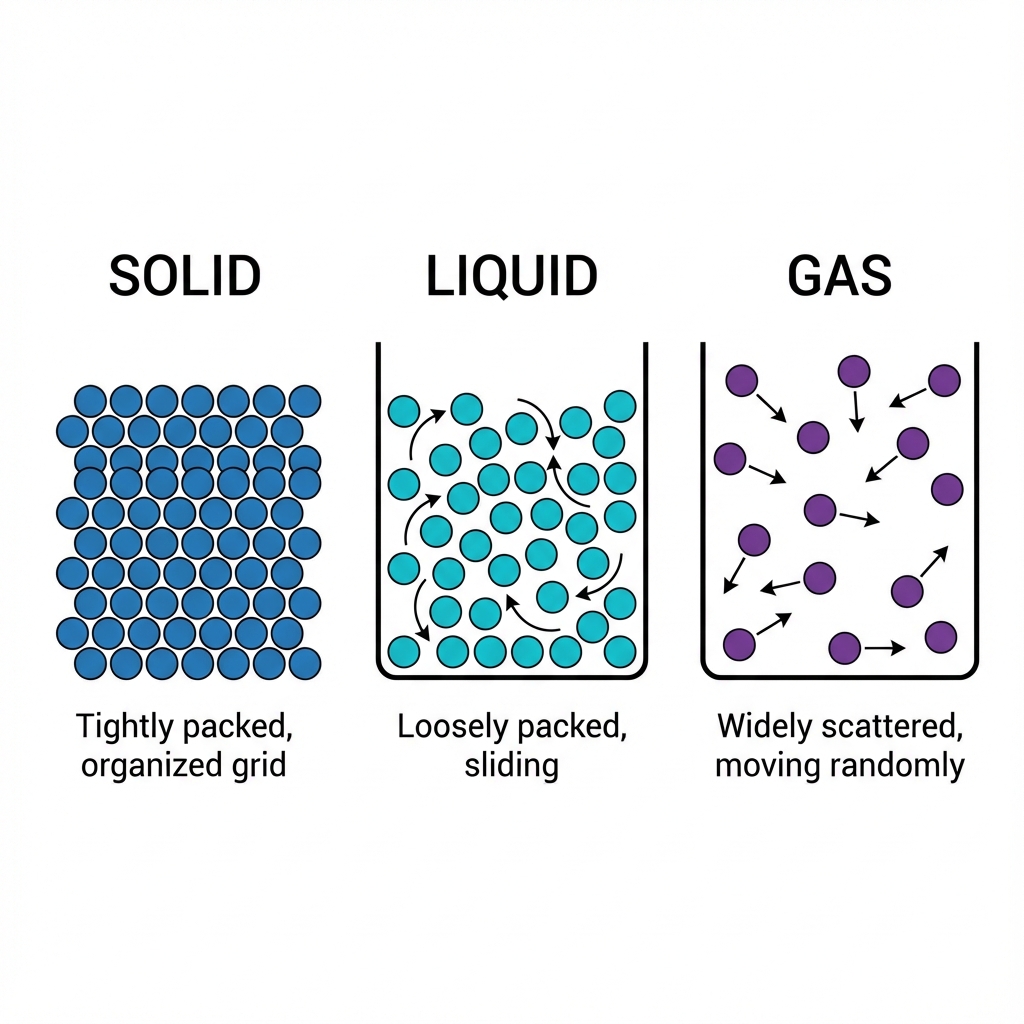
1️⃣ The Solid State 🧊
Properties of Solids
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Shape | Definite, fixed shape |
| Boundaries | Distinct boundaries |
| Volume | Fixed volume |
| Compressibility | Negligible (cannot compress) |
| Rigidity | Maintains shape under force |
Examples
- Pen, Book, Needle, Wooden stick
Special Cases
Q: Is rubber band solid?
Yes! It changes shape under force but regains it when released.
Q: Sugar takes shape of jar. Is it solid?
Yes! Each individual crystal has fixed shape.
Q: Sponge is compressible. Is it solid?
Yes! It has tiny holes with trapped air. When pressed, air is expelled.
2️⃣ The Liquid State 💧
Properties of Liquids
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Shape | No fixed shape (takes container shape) |
| Volume | Fixed volume |
| Flow | Can flow (fluid) |
| Boundaries | No distinct boundaries |
Key Observations
- Liquids flow and change shape
- Volume remains same in different containers
- Liquids are not rigid but are fluid
Diffusion in Liquids
- Rate of diffusion: Liquids > Solids
- Oxygen and CO₂ dissolve in water (essential for aquatic life!)
3️⃣ The Gaseous State 💨
Properties of Gases
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Shape | No fixed shape |
| Volume | No fixed volume |
| Compressibility | Highly compressible |
| Diffusion | Very fast |
| Pressure | Exerts pressure on container walls |
🧪 Activity 1.11: Compressing Different States
Using syringes with:
- Air (gas) → Easily compressed ✅
- Water (liquid) → Difficult to compress
- Chalk (solid) → Cannot compress ❌
Real-Life Applications
| Compressed Gas | Use |
|---|---|
| LPG | Cooking cylinders |
| Oxygen | Hospital cylinders |
| CNG | Vehicle fuel |
Due to high compressibility, large volumes of gas fit in small cylinders!