Module 1: Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Introduction to Matter
introduction-to-matter
Physical Nature of Matter
physical-nature-of-matter
Particles Have Space Between Them
particles-have-space
Particles Attract Each Other
particles-attract
States of Matter
states-of-matter
Change of State: Effect of Temperature
change-of-state-temperature
Sublimation and Effect of Pressure
sublimation-pressure
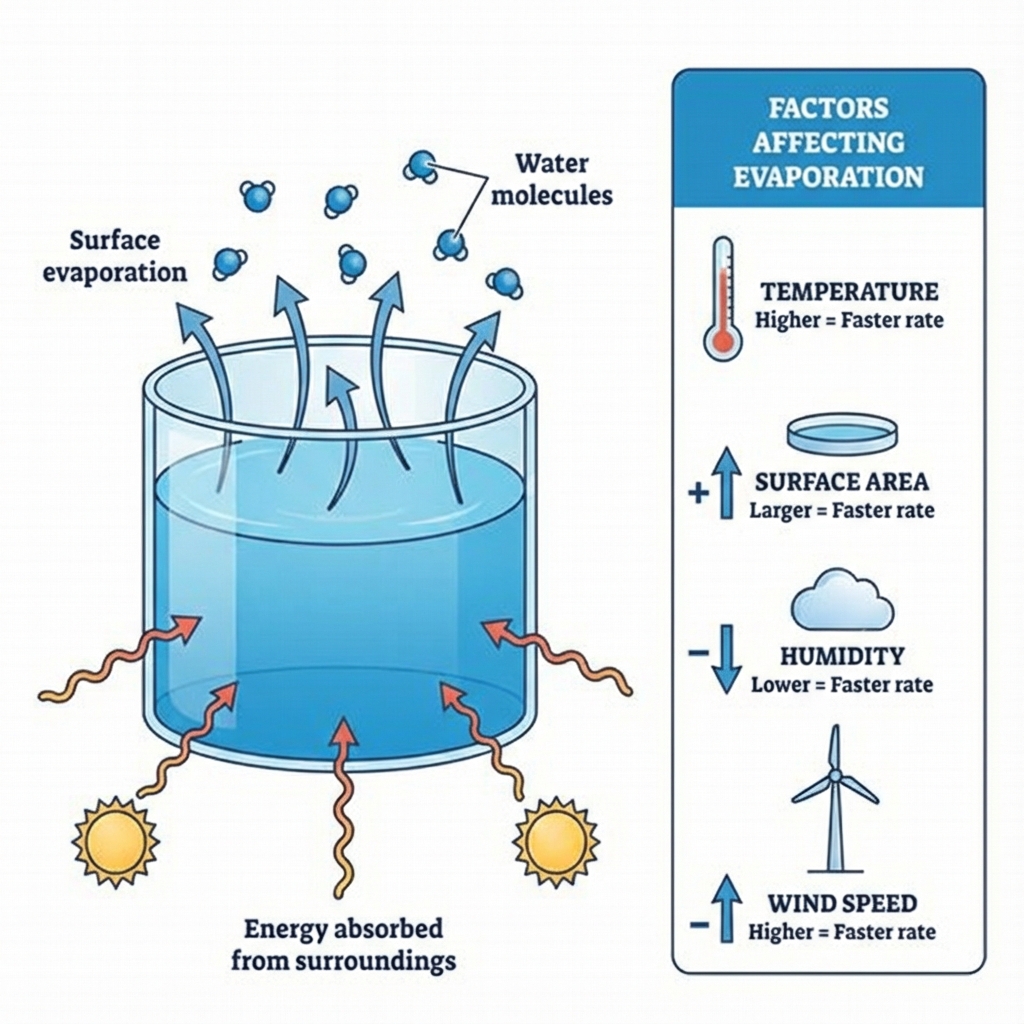
Evaporation
evaporation
Summary & Practice Questions
summary-questions
Module 2: Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Pure Substances & Mixtures
pure-substances-mixtures
Types of Mixtures
types-of-mixtures
What is a Solution?
what-is-solution
Concentration of Solutions
concentration-of-solutions
Suspensions & Colloids
suspensions-colloids
Separation Techniques - Part 1
separation-techniques-1
Separation Techniques - Part 2
separation-techniques-2
Crystallisation
crystallisation
Physical & Chemical Changes
physical-chemical-changes
Elements & Compounds
elements-compounds
Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Separation Techniques - Part 1
Separating Components of Mixtures 🔬
Different methods are used to separate components based on their properties.
1. Evaporation
Used for: Separating volatile solvent from non-volatile solute
Example: Salt from salt solution
Easy Diagram for Exam:
Heat source + Water evaporates
↑ ↑↑↑↑↑
┌─────────────────┐
│ ~~ Salt water ~~│ ← Salt solution
│ ═══════════ │
└─────────────────┘
China dish
↓
Salt remains behind
2. Centrifugation
Used for: Separating small particles that pass through filter paper
Principle: Denser particles forced to bottom when spun rapidly
Diagram for Centrifuge:
Before Spinning After Spinning
┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ │ │ │
│ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ │ →→ │ clear │
│ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ │ SPIN │ liquid │
│ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ ∘ │ │───────────│
└───────────┘ │ sediment │
Mixed └───────────┘
📝 Exam point: Heavier particles settle at bottom
Applications:
- 🥛 Separating cream from milk
- 🩸 Blood and urine tests in labs
3. Separating Funnel
Used for: Separating immiscible liquids (oil and water)
Diagram for Separating Funnel:

Cap/Stopper
│
┌─────┴─────┐
│ ░░░░░░░░░ │ ← Oil (lighter, floats)
│ ░░░░░░░░░ │
│───────────│ ← Boundary
│ ▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓ │ ← Water (denser, sinks)
│ ▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▓ │
\ │ /
\ │ /
\ │ /
\ │ /
\│/
▼
Stopcock
│
Water drains
first
📝 Important: Water (denser) at bottom, oil (lighter) at top
4. Sublimation
Used for: Separating substances that sublime (solid → gas directly)
Diagram for Sublimation:
┌─────────────────┐
│ Inverted funnel │ ← Camphor collects here
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ╲ ╱ │ (as solid again)
│ ╲ ╱ │
└───────┴───┴──────┘
┌─────────────────┐
│ Camphor + Salt │
│ ● ○ ● ○ ● ○ │
└─────────────────┘
🔥 Heat
Salt remains, Camphor deposits on funnel
Sublimable substances: Camphor, Naphthalene, Ammonium chloride