Module 1: Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Introduction to Matter
introduction-to-matter
Physical Nature of Matter
physical-nature-of-matter
Particles Have Space Between Them
particles-have-space
Particles Attract Each Other
particles-attract
States of Matter
states-of-matter
Change of State: Effect of Temperature
change-of-state-temperature
Sublimation and Effect of Pressure
sublimation-pressure
Evaporation
evaporation
Summary & Practice Questions
summary-questions
Module 2: Chapter 2: Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Pure Substances & Mixtures
pure-substances-mixtures
Types of Mixtures
types-of-mixtures
What is a Solution?
what-is-solution
Concentration of Solutions
concentration-of-solutions
Suspensions & Colloids
suspensions-colloids
Separation Techniques - Part 1
separation-techniques-1
Separation Techniques - Part 2
separation-techniques-2
Crystallisation
crystallisation
Physical & Chemical Changes
physical-chemical-changes
Elements & Compounds
elements-compounds
Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Evaporation
What is Evaporation?
Evaporation is the change of liquid into vapour at any temperature below its boiling point.
Examples in Daily Life:
- Uncovered water slowly disappears
- Wet clothes dry up
- Puddles disappear on sunny days
Evaporation vs Boiling 📊
| Property | Evaporation | Boiling |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Surface phenomenon | Bulk phenomenon |
| Temperature | Below boiling point | At boiling point |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Location | Only from surface | Throughout liquid |
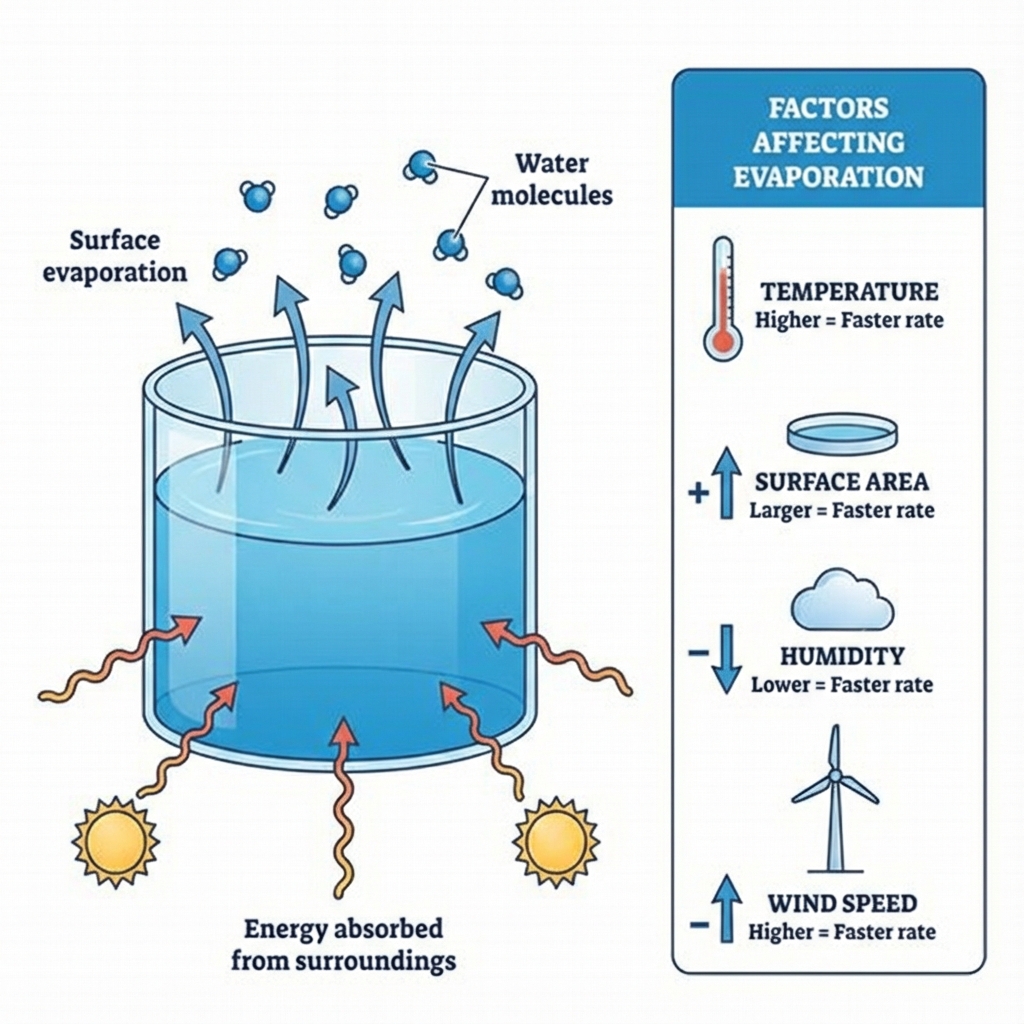
Factors Affecting Evaporation 🌡️
🧪 Activity 1.14: Testing Evaporation
Setup: 5 mL water in different conditions
1️⃣ Surface Area ↗️
More surface area = Faster evaporation
Example: We spread clothes to dry them
2️⃣ Temperature ↗️
Higher temperature = Faster evaporation
More particles get enough kinetic energy to escape
3️⃣ Humidity ↘️
Lower humidity = Faster evaporation
Humidity = Amount of water vapour in air
4️⃣ Wind Speed ↗️
Higher wind speed = Faster evaporation
Wind carries away the water vapour
Evaporation Causes Cooling ❄️
Why does evaporation cause cooling?
- Liquid particles at surface gain energy from surroundings
- They escape as vapour
- This energy (latent heat of vaporisation) is absorbed from the surroundings
- Surroundings become cooler!
Real-Life Applications 🌍
Why do we feel cold with acetone on palm?
Acetone evaporates quickly, absorbing heat from your hand
Why sprinkle water on hot ground?
Water evaporation absorbs heat, cooling the ground
Why wear cotton clothes in summer?
Cotton absorbs sweat and exposes it for evaporation, cooling us
Why do desert coolers work better on hot dry days?
Low humidity = faster evaporation = more cooling!
Why is earthen pot water cool?
Porous pot allows water to seep and evaporate outside
Why can we sip hot tea faster from saucer than cup?
Saucer has larger surface area = faster evaporation = cools faster
Water Droplets on Cold Glass 💧
Why do we see water droplets on a glass of ice-cold water?
Water vapour in air touches cold glass → Loses energy → Condenses to liquid droplets!
This is condensation — the reverse of evaporation.